Research
The Anti-angiogenic Effect of
Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Michihiko Kuwano
Professor, Dean, Faculty of Medical Sciences
|
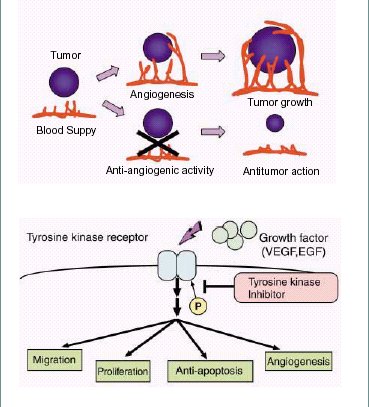
What is angiogenesis ?
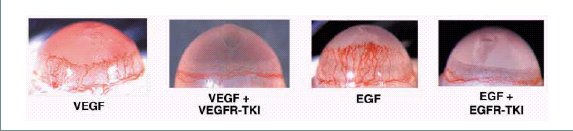
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) inhibitor targets
KDR tyrosine kinase. We demonstrated that a potent VEGFR
tyrosine kinase inhibitor (VEGFR-TKI) also blocks Flt-1tyrosine
kinase, which is another VEGF receptor. This compound inhibits
migration of vascular endothelial cells and monocytes
macrophages in response to placenta growth factor (PlGF).
Moreover, this compound inhibits PlGF-induced angiogenesis in
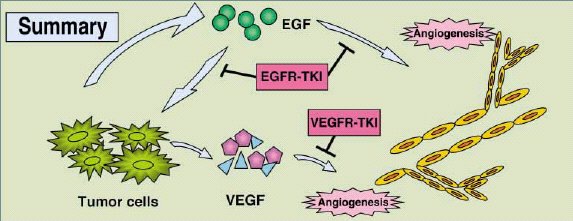
Matrigel plug assay. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase is a potential target for anticancer therapy. We demonstrated that the antitumor effects of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) could be mediated in part by inhibition of tumor angiogenesis through direct effects on vascular endothelial cells (EGFR-TKI inhibited EGF-induced formation of tube-like structures ) and also through reduced production of proangiogenic factors (VEGF, IL-8) by tumor cells. |
|
|
Dr. Michihiko Kuwano, Dean of
Faculty of Medical Sciences
explains here how the science
battles with cancer. This research
theme was chosen for one of the
*P&P projects in 98-99. *P&P: Kyushu University's grant for faculties to promote research and education, which started in 1997. |
  |