selected for the 21st Century COE Program
|
Field of study : Medical Sciences

| Program Title | Frontier Research and Education on Lifestyle-Related Diseases based on the Large-scale Cohort Study(Japanese only) |
| The core courses to form the program | Department of Medicine and Surgery, Graduate School of Medical Sciences |
| Program Leader | Prof. Hajime Nawata |
Program Summary
The conquest of gthe lifestyle-related diseasesh such as stroke, myocardial infarction, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia and cancer represents a challenge for maintaining the hearth and vitality of the nation. The lifestyle-related diseases are caused and developed by the intricate interaction between polygenetic and environmental (regionality, eating habits, ethnic difference, etc) factors. Therefore, to overcome the lifestyle-related diseases, their pathogenic characteristic of Japanese population must be clarified by analyzing the longitudinally accumulated epidemiological and clinical data, and human genomes, thereby enabling the development of therapy and prophylaxis.
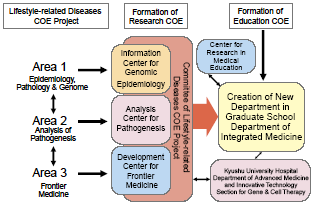 The Hisayama study, which is the world-famous clinicopathological and epidemiological research, and research and
education on vascular disease peculiar to Japanese, diabetes mellitus and cancer has been conducted for over 40 years in Kyushu University.
The Hisayama study, which is the world-famous clinicopathological and epidemiological research, and research and
education on vascular disease peculiar to Japanese, diabetes mellitus and cancer has been conducted for over 40 years in Kyushu University.In our project, researche is performed in three areas, Area 1: epidemiology, pathology and genome, Area 2: analysis of pathogenesis, and Area 3: frontier medicine. We will form gCOE (the center of excellence) for Frontier Research and Education on Lifestyle-Related Diseases of Japaneseh by cooperation and integration of these three areas. Especially, as completion of Area 1, we will organize the large-scale cohort in Kyushu and establish gThe Information Center for Genomic Epidemiology in Kyushu Universityh which has clinical and genomic databases constructed in a common format. We provide educational courses for Areas 1, 2 and 3, which train doctor course students to be able to conduct research all in the three areas, as well as to be an expert at a specific area.
Field of study : Mathematics, Physics, Earth science

| Program Title | Development of Dynamic Mathematics with High Functionality |
| The core courses to form the program | Department of Mathematics, Graduate School of Mathematics |
| Program Leader | Prof. Mitsuhiro Nakao |
Program Summary
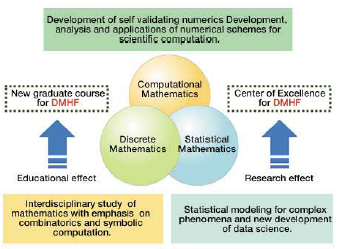 Historically, research in mathematics has been often stimulated by the development of other sciences. Especially, recent rapid progress in the computer has brought new insights to some branches in mathematics, which used to be simply out of our reach. Studies in other disciplines of science are largely based on analysis on suitable mathematical models, and conversely mathematics is expected to be able to make such modeling possible with the help of the computer. Under these circumstances our department has been maintaining strong programs in computational, statistical and discrete mathematics. By making full use of advantage of this accumlated experience, we would like to strengthen our current programs further to deal with diverse complexity appearing in natural, social and information sciences. We would like to call such a discipline gDynamic Mathematics with High Functionality, DMHF.h Development of the discipline together with reform of our graduate program suited for this purpose will make our department an international core institution in research as well as education. We believe that such a change will meet social demand in the new century. This COE program will impact on other disciplines of science as well as traditional mathematics such as algebra, geometry and analysis.
Historically, research in mathematics has been often stimulated by the development of other sciences. Especially, recent rapid progress in the computer has brought new insights to some branches in mathematics, which used to be simply out of our reach. Studies in other disciplines of science are largely based on analysis on suitable mathematical models, and conversely mathematics is expected to be able to make such modeling possible with the help of the computer. Under these circumstances our department has been maintaining strong programs in computational, statistical and discrete mathematics. By making full use of advantage of this accumlated experience, we would like to strengthen our current programs further to deal with diverse complexity appearing in natural, social and information sciences. We would like to call such a discipline gDynamic Mathematics with High Functionality, DMHF.h Development of the discipline together with reform of our graduate program suited for this purpose will make our department an international core institution in research as well as education. We believe that such a change will meet social demand in the new century. This COE program will impact on other disciplines of science as well as traditional mathematics such as algebra, geometry and analysis.
Field of study : Mechanical, Civil, Construction and Others engineering

| Program Title | Architecture of Habitat System for Sustainable Development |
| The core courses to form the program | Department of Architecture, Graduate School of Human-Environment Studies |
| Program Leader | Prof. Yasunori Matsufuji |
Program Summary
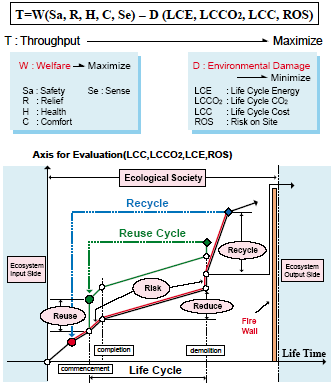 Our target is the whole habitat system from a single architecture to the regional community as an organic entity of architectures. We propose a methodology for sustainable development of our habitat system by reducing environmental damage together with maintaining the optimal level of modern quality of life, which will help in constructing an ecological society.
Our target is the whole habitat system from a single architecture to the regional community as an organic entity of architectures. We propose a methodology for sustainable development of our habitat system by reducing environmental damage together with maintaining the optimal level of modern quality of life, which will help in constructing an ecological society.To determine the optimal solution for a complex ecosystem we need a unified evaluation strategy. We use our original gthroughput formula,h in which we maximize the difference (T: throughput) between the quality of life (W: welfare) and environmental damage (D: damage). We can use this fundamental formula as a tool to evaluate and manage any sustainable habitat system developments. For logical and objective dicision making we must create a way to translate different dimensions of W and D into common indeces. This fundamental formula will work as a scale to measure ecological throughput of our activities for the whole life cycle of any habitat systems. Outcome of our project will be a base for a new educational program on gSustainable Architecture,h which will produce new-generation engineers for sustainable habitat systems.
Field of study : Mechanical, Civil, Construction and Others engineering

| Program Title | Integration Technology of Mechanical Systems for Hydrogen Utilization |
| The core courses to form the program | Department of Mechanical Engineering Science, Graduate School of Engineering |
| Program Leader | Prof. Yukitaka Murakami |
Program Summary
 We have only just set out on the road to becoming a ghydrogen society,h - one which uses hydrogen as the energy source. With recent popularization of the fuel cell car, construction of the manufacturing and transportation systems for hydrogen is going into full swing.
We have only just set out on the road to becoming a ghydrogen society,h - one which uses hydrogen as the energy source. With recent popularization of the fuel cell car, construction of the manufacturing and transportation systems for hydrogen is going into full swing.It is vital for such a society to have the technology that can treat hydrogen safely as well as the basic technology to develop individual equipment. However, the deepening and the differentiation of the scientific technology in recent years are bringing the loss of general scholarly viewpoint, which the mechanical engineering should have originally, and are increasing horrible accidents.
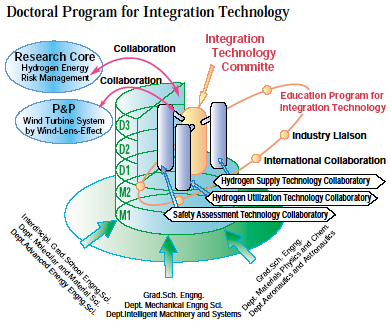
This COE program is the one that will form the center of excellence, which will head the world for the hydrogen society to realize by challenging the building of the mechanical systems for hydrogen utilization, which are indispensable to form the sustainable society in the 21st century.
We perform research in three co-laboratories for gHydrogen Utilization,h gHydrogen Supplyh and gSafety Evaluation.h Simultaneously we place gBoard for Integration Technology,h which controls these three co-laboratories to perform the research and practice on the integration of the differentiating theories and technologies.
As an educational feature of the graduate school, we provide an gIntegration Technology Course,h which requires the doctor course students to attend the gBoard for Integration Technologyh and therein educates to have the ability to integrate different expertise, as well as to deepen individual expertise on the mechanical systems for hydrogen utilization.
Field of study : Interdisciplinary, Combined Fields, New Disciplines

| Program Title | Design of artificial environments on the basis of human sensibility |
| The core courses to form the program | Graduate School of Design |
| Program Leader | Prof. Yutaka Tochihara |
Program Summary
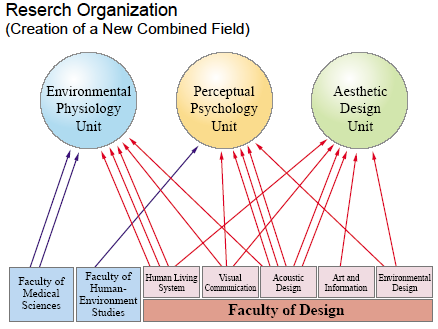 Our everyday life is increasingly dependent on artificial environments, and often human sensibility is neglected when convenience or economy has priority. For example, artificial lighting can violate human biological rhythms, and excessive use of artificial images and sounds can cause nervous disorders or hearing impairments.
Our everyday life is increasingly dependent on artificial environments, and often human sensibility is neglected when convenience or economy has priority. For example, artificial lighting can violate human biological rhythms, and excessive use of artificial images and sounds can cause nervous disorders or hearing impairments.Kyushu University, with its Faculty of Design, whose ultimate purpose is to "humanize modern technology," has been building an ideal environment to tackle such problems in an interdisciplinary manner. We have thus decided to rebuild our organization as a bridgehead for international cooperation for research and education in related areas. We try to increase our understanding of human sensibility by conducting physiological and psychological experiments, and the knowledge obtained is applied to the actual design of artificial environments directly.
Our team is divided into three research units in order to work efficiently, i.e. the units of "environmental physiology," "perceptual psychology," and "aesthetic design." The members of the first two units study human vision, audition, olfaction, temperature sensation, somatic sensation etc, and those belonging to the last unit-design lighting, images, sounds, air conditioning, architecture, etc. We evaluate various artificial environments from a global viewpoint, and draw guidelines to design suitable environments especially for young children, senior citizens, and the disabled.
Educating doctoral students and postdoctoral researchers is also an important aspect of our project. We receive students and young researchers from all over the world, and train them in such a way that they gain experience in at least two of the three above-mentioned research units. This will enable us to organize small but productive collaboration teams easily. We try to use both Japanese and English for communication in order to make our project really international.