研究成果 Research Results
- TOP
- News
- Research Results
- The regulation mechanism of the NF-κB-like transcription factor Relish through the polyamine-modification catalyzed by transglutaminase
The regulation mechanism of the NF-κB-like transcription factor Relish through the polyamine-modification catalyzed by transglutaminase
2017.04.14Research ResultsLife & Health
Drosophila has an immune signal pathway, called the immune deficiency (IMD) pathways. The final IMD pathway-dependent signal is transmitted through proteolytic conversion of the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)-like transcription factor Relish to the active N-terminal fragment Relish-N. Relish-N is then translocated from the cytosol into the nucleus for the expression of IMD-controlled genes. We previously demonstrated that transglutaminase (TG) suppresses the IMD pathway by polymerizing Relish-N to inhibit its nuclear translocation. On the other hand, we also demonstrated that orally ingested synthetic amines are TG-dependently incorporated into Relish-N. It remains unclear, however, whether polyamine-containing Relish-N retains transcriptional activity. Here we used mass spectrometry analysis and recombinant proteins, and show that the TG-modified Gln residues are located in the DNA-binding region of Relish-N. Moreover, in vivo experiments demonstrated that Relish-N was TG-dependently modified by polyamines, and that this modification reduced transcription of IMD pathway-controlled antimicrobial peptide genes. These findings suggest that TG regulates Relish-N-mediated transcriptional activity by incorporating polyamines into Relish-N and via protein-protein crosslinking.
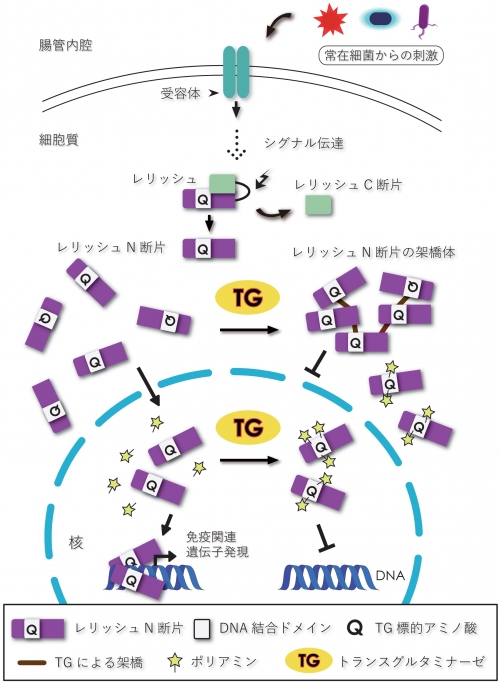
TG-catalyzed regulation of the IMD pathway in Drosophila
Journal Reference
The regulation mechanism of the NF-κB-like transcription factor Relish through the polyamine-modification catalyzed by transglutaminase, ,the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (ASBMB), 10.1074/jbc.M117.779579Research-related inquiries
- TOP
- News
- Research Results
- The regulation mechanism of the NF-κB-like transcription factor Relish through the polyamine-modification catalyzed by transglutaminase