研究成果 Research Results
- TOP
- News
- Research Results
- The mechanism of DNA methylation changes in germ cell differentiation in a culture dish -A resource to understand and overcome infertility-
The mechanism of DNA methylation changes in germ cell differentiation in a culture dish -A resource to understand and overcome infertility-
2016.09.20Research ResultsLife & Health
Our body is derived from one fertilized egg, which is formed by fusing a sperm cell and an egg. During the differentiation of germ cells, which are the origins of sperm and eggs, DNA methylation, which is an important mark for modulating gene function, changes dynamically. However, it has been difficult to know the underlying mechanism due to the limited number of germ cells. In 2011, the group of Professor Mitinori Saitou and Associate Professor Katsuhiko Hayashi (now a Professor in Kyushu University) in Kyoto University developed a method to derive germ cells from mouse pluripotent stem cells in a culture dish. The produced germ cells can be further differentiated into functional sperm or eggs through transplantation into live mice. However, the characterization of the germ cells produced in a dish was an urgent issue.
In this study, the group of Distinguished Professor Hiroyuki Sasaki (also Vice President of Kyushu University) and a graduate student Kenjiro Shirane revealed that the produced cells recapitulate the DNA methylation change that occurs at the outset of germ cell differentiation. The group also identified a regulator of the DNA methylation change using the culture system. The data obtained in this study would be a useful resource for future studies of human germ cell differentiation and would contribute to the elucidation of the cause of infertility and the development of a new therapeutic strategy for the disease.
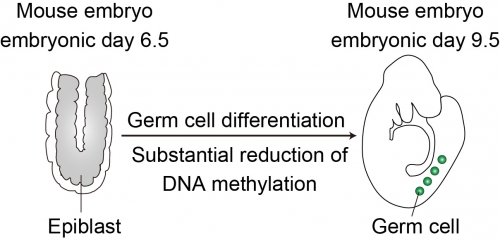
Germ cells are derived from somatic cells called epiblast. During this process, the DNA methylation level is substantially reduced. In this study, we used a cell culture system that recapitulates the germ cell differentiation in mice to understand the underlying mechanism. Our system should be useful to study human infertility.
Researcher comments
Germ cells produced in a culture dish will enable us to address many fundamental questions. Uncovering the mechanism of the DNA methylation change in germ cells and the identification of its regulator are the important outcomes of the study. We hope that this system will facilitate the study of germ cell differentiation and infertility in human.
Journal Reference
Global Landscape and Regulatory Principles of DNA Methylation Reprogramming for Germ Cell Specification by Mouse Pluripotent Stem Cells, ,Developmental Cell, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2016.08.008Research-related inquiries
- TOP
- News
- Research Results
- The mechanism of DNA methylation changes in germ cell differentiation in a culture dish -A resource to understand and overcome infertility-