研究成果 Research Results
- TOP
- News
- Research Results
- Intronic regulation of Aire expression by Jmjd6 for self-tolerance induction in the thymus
Intronic regulation of Aire expression by Jmjd6 for self-tolerance induction in the thymus
2015.11.05Research ResultsLife & Health
A research team including Distinguished Professor Yoshinori Fukui of the Kyushu University Medical Institute of Bioregulation and Kyushu University graduate student Toyoshi Yanagihara has discovered a new mechanism required to ensure that white blood cells called T-cells acquire a function called self-tolerance, which prevents them attacking the body.
Autoimmune diseases arise when the body’s immune response turns against its own organs, which it should not attack. The place where T-cells are taught not to attack the body’s own organs is an organ called the thymus, but the mechanism via which this education takes place was unknown. Focusing on a protein called Jmjd6, which is expressed in thymic epithelial cells and plays a part in educating developing T-cells in the thymus, the research team analyzed the role of this protein. As a result, it discovered that the absence of Jmjd6 substantially inhibits expression of a protein called Aire, which plays a part in inducing self-tolerance. Furthermore, a detailed analysis ascertained that, unlike Jmjd6’s known method of inhibition, it controls the level of expression of the protein Aire via post-transcriptional regulation through intron retention.
It is hoped that this knowledge will substantially advance understanding of the onset mechanism of autoimmune diseases.
The outcomes of this study were published in the online edition of the British scientific journal Nature Communications at 10:00 (UK time) on Wednesday, November 4, 2015.
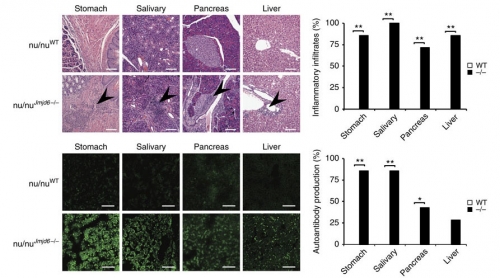
Haematoxylin and eosin staining of tissues from nu/nuWT and nu/nuJmjd6−/− mice. Scale bars, 100 μM. The percentage of each organ with inflammatory infiltrates was compared between nu/nuWT (n=8) and nu/nuJmjd6−/− (n=7) mice.
Immunofluorescence staining showing the presence of autoantibodies (green) in nu/nuJmjd6−/− mice. Scale bars, 100 μM. The percentage of mice with autoantibodies against each tissue was compared between nu/nuWT (n=8) and nu/nuJmjd6−/− mice (n=7). Data are collected from four (a), six (c–g) and three
Note:separate experiments and are expressed as mean±s.d. *P<0.05; **P<0.01 (two-tailed Student’s t-test).
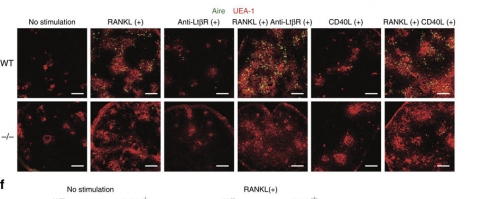
Following stimulation with RANKL, anti-LtβR antibody and/or CD40L for 4 days, 2-DG-treated fetal thymic stroma from WT and Jmjd6−/− embryos were stained with UEA-1 and anti-Aire antibody. Scale bars, 50 μM.
Journal Reference
Intronic regulation of Aire expression by Jmjd6 for self-tolerance induction in the thymus, ,Toyoshi Yanagihara and Fukui Yoshinori et al., Nature Communications, 10.1038/NCOMMS9820Research-related inquiries
- TOP
- News
- Research Results
- Intronic regulation of Aire expression by Jmjd6 for self-tolerance induction in the thymus