研究成果 Research Results
- TOP
- News
- Research Results
- Phosphorylation of EB2 by Aurora B and CDK1 ensures mitotic progression and genome stability
Phosphorylation of EB2 by Aurora B and CDK1 ensures mitotic progression and genome stability
2016.03.31Research ResultsLife & Health
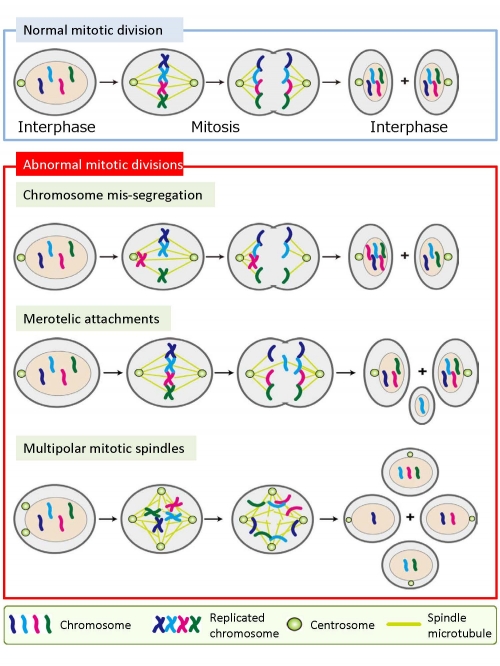
Temporal regulation of microtubule dynamics is essential for proper progression of mitosis and control of microtubule plus-end tracking proteins by phosphorylation is an essential component of this regulation. Here we show that Aurora B and CDK1 phosphorylate microtubule end-binding protein 2 (EB2) at multiple sites within the amino terminus and a cluster of serine/threonine residues in the linker connecting the calponin homology and end-binding homology domains.
EB2 phosphorylation, which is strictly associated with mitotic entry and progression, reduces the binding affinity of EB2 for microtubules. Expression of non-phosphorylatable EB2 induces stable kinetochore microtubule dynamics and delays formation of bipolar metaphase plates in a microtubule binding-dependent manner, and leads to aneuploidy even in unperturbed mitosis.
We propose that Aurora B and CDK1 temporally regulate the binding affinity of EB2 for microtubules, thereby ensuring kinetochore microtubule dynamics, proper mitotic progression and genome stability.
Mitotic division stages
Journal Reference
Phosphorylation of EB2 by Aurora B and CDK1 ensures mitotic progression and genome stability, ,Nature Communications,Research-related inquiries
Yoshihiko Maehara, Professor, Faculty of Medical Sciences
Makoto Iimori, Assistant Professor, Faculty of Medical Sciences
Makoto Iimori, Assistant Professor, Faculty of Medical Sciences
- TOP
- News
- Research Results
- Phosphorylation of EB2 by Aurora B and CDK1 ensures mitotic progression and genome stability